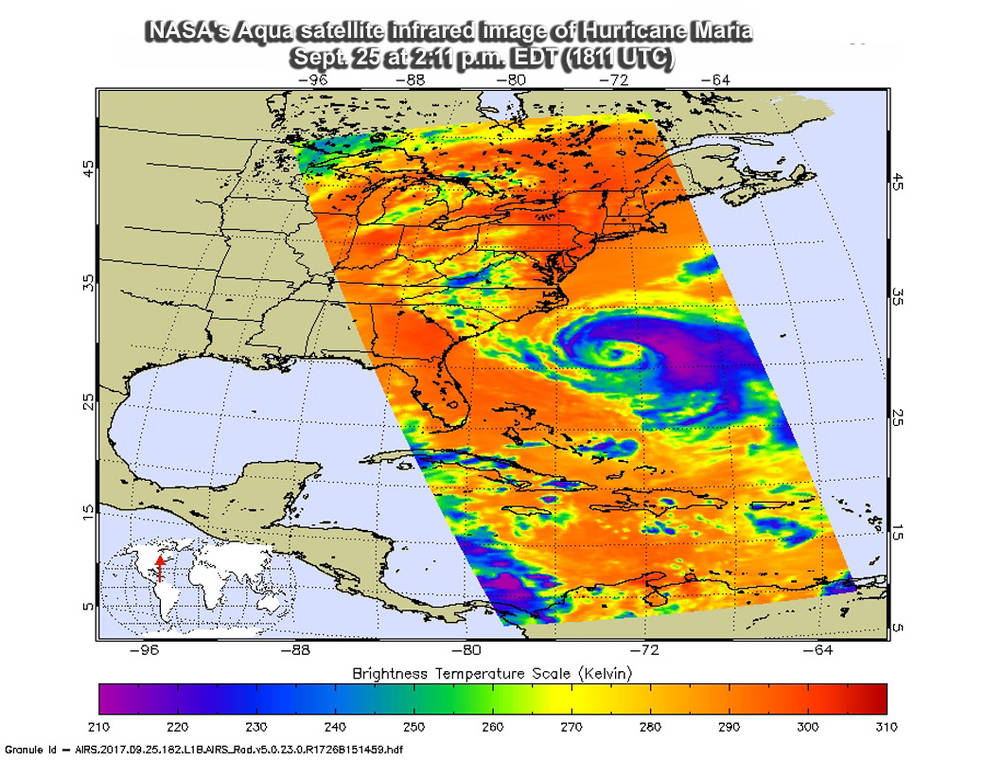
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Maria on Sept. 25 at 2:11 p.m. EDT (1811 UTC) and analyzed the storm in infrared light. Infrared light provides scientists with temperature data, important when trying to understand storm intensity. The lowest temperatures, in dark purple, are associated with the high, cold cloud tops of powerful thunderstorms with heavy rainfall potential. So infrared light as that gathered by the AIRS instrument can identify the strongest sides of a tropical cyclone. The AIRS image clearly showed the bulk of strong storms in Maria's northeastern quadrant as well as in the storms surrounding the eye.
Image Date:
Monday, September 25, 2017